[T101 4기] 테라폼으로 AWS EKS 배포
들어가며
이번 주에는 테라폼으로 AWS EKS 배포를 하는것을 테라폼으로 시작하는 IaC를 통해 알아 보겠습니다.
Amazon EKS Blueprints for Terraform
개요
- Amazon EKS BluePrints 소개 Link / FAQ Link
- Amazon EKS Blueprints for Terraform은 Terraform으로 Amazon EKS 클러스터를 구축하는 패턴들의 모음이며, Amazon EKS를 도입하는것이 얼마나 빠르고 쉬운지 보여줍니다.
- 사용 방법은 Amazon EKS Blueprints를 참고해서 원하는 패턴을 선택하고 Terraform을 사용해서 클러스터를 구축하는 방법과, 필요한 스니펫들을 복사해서 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 주의할 점
- Amazon EKS Blueprints는 AWS CloudFormation을 사용하는 것이 아니라 Terraform을 사용합니다.
- 있는 그대로 사용되는것을 권장하지 않으며, 사용자의 환경에 맞게 수정해서 사용하는것을 권장합니다.
- 패턴과 스니펫은 Terraform 모듈로 설계되지 않았으며, 모듈화를 하려면는 사용자가 직접 수행해야 합니다.
- Local 블록을 주로 사용하며, 특정 정보가 필요한 경우 (Route 53 호스트 영역 ID 등)만 Variable 블록을 사용합니다.
- 복잡성을 줄이기위해 variable과 outputs가 최대한 사용되지 않았습니다.
[실습] EKS Fargate 및 Karpenter 배포
먼저 EKS와 Fargate, Karpenter에 대해 간략하게 알아보겠습니다.
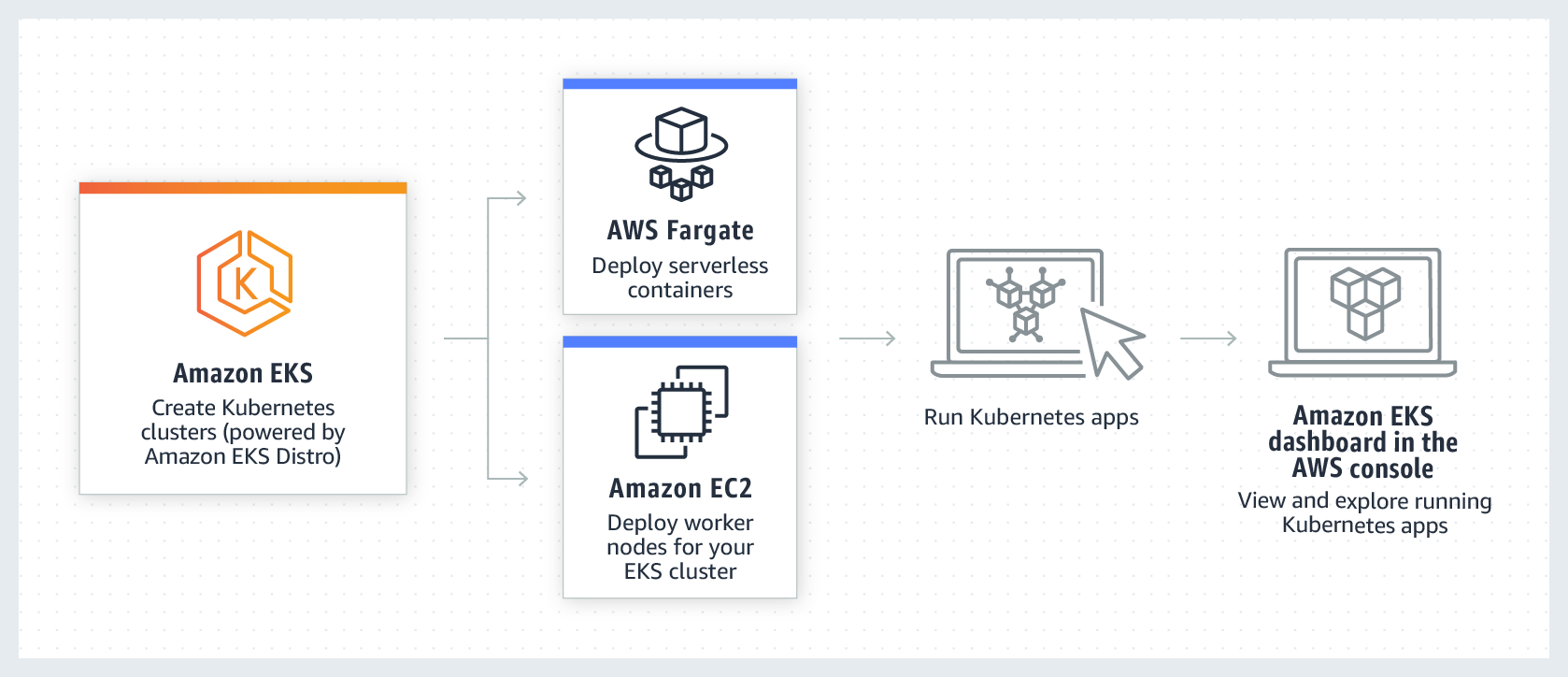
EKS는 Elastic Kubernetes Service의 약자로, AWS에서 제공하는 관리형 Kubernetes 서비스입니다.
EKS를 사용하면 컨테이너 예약, 가용성 관리, 클러스터의 데이터 저장 및 다른 주요 작업을 담당하는 Kubernetes 컨트롤 플레인의
가용성과 확장성을 쉽게 관리할 수 있습니다. EKS는 컨테이너를 EC2 상에서 운영하거나 Fargate를 통해
탄력적으로 서버리스 방식으로 운영할 수도 있습니다.
AWS EKS 소개
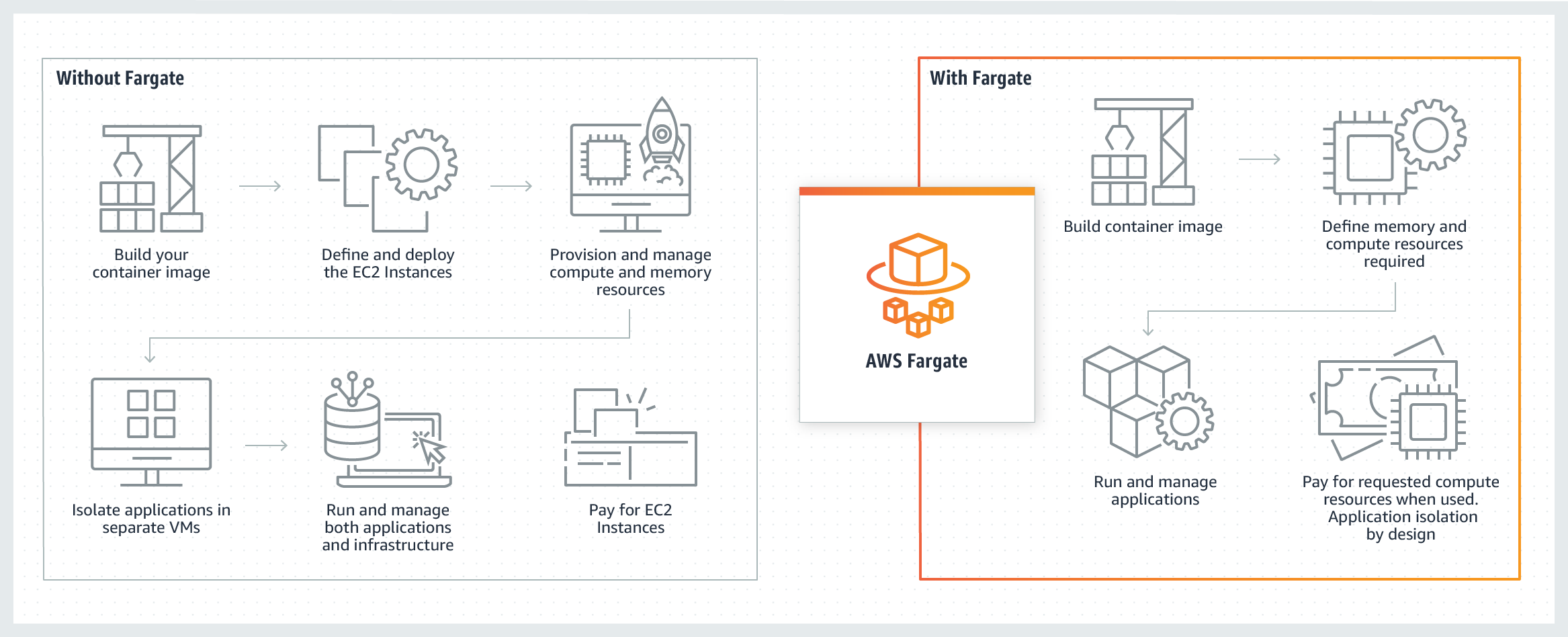
Fargate는 AWS에서 제공하는 서버리스 컴퓨팅 엔진으로, 컨테이너를 별도의 서버 관리 없이, 컨테이너를 사용한 만큼만 비용을 지불할 수 있는 서비스입니다. AWS Fargate 소개
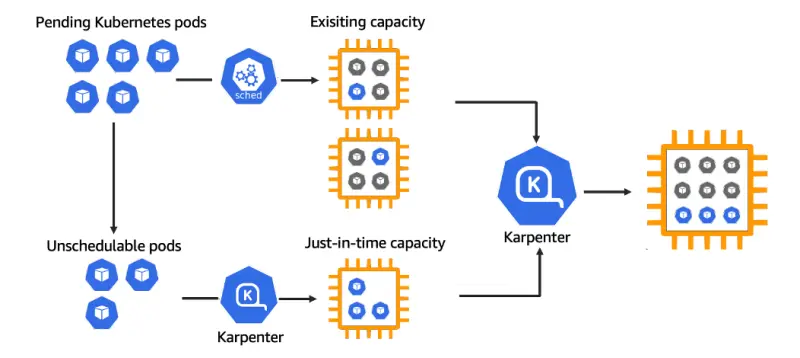
Karpenter는 Kubernetes 클러스터에 동작하는 Node를 최적화하여 효율성과 비용을 최적화하는 오픈소스 프로젝트입니다.
Karpenter는 Node의 리소스 부족으로 스케쥴 되지 못한 pod들을 Node를 추가하여 스케쥴링하는 Autoscaling 기능 뿐만 아니라,
각각 Node들을 조각모음 하듯이 더 크고 저렴한 하나의 노드로 교체하는 등의 전략을 통해 비용을 최적화합니다.
Karpenter 소개
- 이번에 실습할 패턴은
Karpenter를 통하여 Fargate에 서버리스 클러스터를 프로비저닝하는 것으로 먼저 EKS와 Fargate를 배포하고, 그 다음에 Karpenter를 배포하는 것을 실습해보겠습니다.
사전준비
- awscli, terraform, kubectl, helm 등 설치
# 설치된 파일 버전 확인 $ aws --version # => aws-cli/2.17.14 Python/3.11.9 Darwin/22.6.0 source/arm64 $ terraform --version # => Terraform v1.8.5 $ kubectl version --client=true # => Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"22", GitVersion:"v1.22.5", GitCommit:"5c99e2ac2ff9a3c549d9ca665e7bc05a3e18f07e", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-12-16T08:38:33Z", GoVersion:"go1.16.12", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/arm64"} $ helm version # => version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.15.3", GitCommit:"3bb50bbbdd9c946ba9989fbe4fb4104766302a64", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.22.5"} - 코드 준비 - Github
$ git clone https://github.com/aws-ia/terraform-aws-eks-blueprints $ cd terraform-aws-eks-blueprints/patterns/karpenter $ tree- versions.tf
terraform { required_version = ">= 1.3" required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = ">= 5.34" } helm = { source = "hashicorp/helm" version = ">= 2.9" } kubernetes = { source = "hashicorp/kubernetes" version = ">= 2.20" } } # ## Used for end-to-end testing on project; update to suit your needs # backend "s3" { # bucket = "terraform-ssp-github-actions-state" # region = "us-west-2" # key = "e2e/karpenter/terraform.tfstate" # } } -
main.tf
provider "aws" { region = local.region } # Required for public ECR where Karpenter artifacts are hosted provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" alias = "virginia" } provider "kubernetes" { host = module.eks.cluster_endpoint cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(module.eks.cluster_certificate_authority_data) exec { api_version = "client.authentication.k8s.io/v1beta1" command = "aws" # This requires the awscli to be installed locally where Terraform is executed args = ["eks", "get-token", "--cluster-name", module.eks.cluster_name] } } provider "helm" { kubernetes { host = module.eks.cluster_endpoint cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(module.eks.cluster_certificate_authority_data) exec { api_version = "client.authentication.k8s.io/v1beta1" command = "aws" # This requires the awscli to be installed locally where Terraform is executed args = ["eks", "get-token", "--cluster-name", module.eks.cluster_name] } } } data "aws_ecrpublic_authorization_token" "token" { provider = aws.virginia } data "aws_availability_zones" "available" {} locals { # name = "ex-${basename(path.cwd)}" name = "t101-${basename(path.cwd)}" # region = "us-west-2" region = "ap-northeast-2" vpc_cidr = "10.10.0.0/16" azs = slice(data.aws_availability_zones.available.names, 0, 3) tags = { Blueprint = local.name GithubRepo = "github.com/aws-ia/terraform-aws-eks-blueprints" } } ################################################################################ # Cluster ################################################################################ module "eks" { source = "terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws" version = "~> 20.11" cluster_name = local.name cluster_version = "1.30" cluster_endpoint_public_access = true vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id subnet_ids = module.vpc.private_subnets # Fargate profiles use the cluster primary security group so these are not utilized create_cluster_security_group = false create_node_security_group = false enable_cluster_creator_admin_permissions = true fargate_profiles = { karpenter = { selectors = [ { namespace = "karpenter" } ] } kube_system = { name = "kube-system" selectors = [ { namespace = "kube-system" } ] } } tags = merge(local.tags, { # NOTE - if creating multiple security groups with this module, only tag the # security group that Karpenter should utilize with the following tag # (i.e. - at most, only one security group should have this tag in your account) "karpenter.sh/discovery" = local.name }) } ################################################################################ # EKS Blueprints Addons ################################################################################ module "eks_blueprints_addons" { source = "aws-ia/eks-blueprints-addons/aws" version = "~> 1.16" cluster_name = module.eks.cluster_name cluster_endpoint = module.eks.cluster_endpoint cluster_version = module.eks.cluster_version oidc_provider_arn = module.eks.oidc_provider_arn # We want to wait for the Fargate profiles to be deployed first create_delay_dependencies = [for prof in module.eks.fargate_profiles : prof.fargate_profile_arn] eks_addons = { coredns = { configuration_values = jsonencode({ computeType = "Fargate" # Ensure that the we fully utilize the minimum amount of resources that are supplied by # Fargate https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/fargate-pod-configuration.html # Fargate adds 256 MB to each pod's memory reservation for the required Kubernetes # components (kubelet, kube-proxy, and containerd). Fargate rounds up to the following # compute configuration that most closely matches the sum of vCPU and memory requests in # order to ensure pods always have the resources that they need to run. resources = { limits = { cpu = "0.25" # We are targeting the smallest Task size of 512Mb, so we subtract 256Mb from the # request/limit to ensure we can fit within that task memory = "256M" } requests = { cpu = "0.25" # We are targeting the smallest Task size of 512Mb, so we subtract 256Mb from the # request/limit to ensure we can fit within that task memory = "256M" } } }) } vpc-cni = {} kube-proxy = {} } enable_karpenter = true karpenter = { repository_username = data.aws_ecrpublic_authorization_token.token.user_name repository_password = data.aws_ecrpublic_authorization_token.token.password } karpenter_node = { # Use static name so that it matches what is defined in `karpenter.yaml` example manifest iam_role_use_name_prefix = false } tags = local.tags } resource "aws_eks_access_entry" "karpenter_node_access_entry" { cluster_name = module.eks.cluster_name principal_arn = module.eks_blueprints_addons.karpenter.node_iam_role_arn kubernetes_groups = [] type = "EC2_LINUX" } ################################################################################ # Supporting Resources ################################################################################ module "vpc" { source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws" version = "~> 5.0" name = local.name cidr = local.vpc_cidr azs = local.azs private_subnets = [for k, v in local.azs : cidrsubnet(local.vpc_cidr, 4, k)] public_subnets = [for k, v in local.azs : cidrsubnet(local.vpc_cidr, 8, k + 48)] enable_nat_gateway = true single_nat_gateway = true public_subnet_tags = { "kubernetes.io/role/elb" = 1 } private_subnet_tags = { "kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb" = 1 # Tags subnets for Karpenter auto-discovery "karpenter.sh/discovery" = local.name } tags = local.tags } - output.tf
output "configure_kubectl" { description = "Configure kubectl: make sure you're logged in with the correct AWS profile and run the following command to update your kubeconfig" value = "aws eks --region ${local.region} update-kubeconfig --name ${module.eks.cluster_name}" }
- versions.tf
- init
$ terraform init $ tree .terraform $ cat .terraform/modules/modules.json | jq $ tree .terraform/providers/registry.terraform.io/hashicorp -L 2
VPC 배포
# VPC 배포전 VPC 확인
$ aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filter 'Name=isDefault,Values=false' --output yaml
# => Vpcs: []
# vpc 배포
$ terraform apply -target="module.vpc" -auto-approve
# 배포 확인
$ terraform state list
$ terraform show
# VPC 정보 확인
$ aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filter 'Name=isDefault,Values=false' --output yaml
# => Vpcs:
# - CidrBlock: 10.10.0.0/16
# CidrBlockAssociationSet:
# - AssociationId: vpc-cidr
# ...
# 상세정보 확인
$ echo "data.aws_availability_zones.available" | terraform console
# => {
# "all_availability_zones" = tobool(null)
# "exclude_names" = toset(null) /* of string */
# "exclude_zone_ids" = toset(null) /* of string */
# "filter" = toset(null) /* of object */
# "group_names" = toset([
# "ap-northeast-2",
# ])
# "id" = "ap-northeast-2"
# "names" = tolist([
# "ap-northeast-2a",
# "ap-northeast-2b",
# "ap-northeast-2c",
# "ap-northeast-2d",
# ])
# "state" = tostring(null)
# "timeouts" = null /* object */
# "zone_ids" = tolist([
# "apne2-az1",
# "apne2-az2",
# "apne2-az3",
# "apne2-az4",
# ])
# }
$ terraform state show 'module.vpc.aws_vpc.this[0]'
$ VPCID=$(echo 'module.vpc.vpc_id' | terraform console)
$ aws ec2 describe-subnets --filters "Name=vpc-id,Values=$VPCID" | jq
$ aws ec2 describe-subnets --filters "Name=vpc-id,Values=$VPCID" --output text
# public 서브넷과 private 서브넷 CIDR 확인
## private_subnets = [for k, v in local.azs : cidrsubnet(local.vpc_cidr, 4, k)]
## public_subnets = [for k, v in local.azs : cidrsubnet(local.vpc_cidr, 8, k + 48)]
$ terraform state show 'module.vpc.aws_subnet.public[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.vpc.aws_subnet.private[0]'
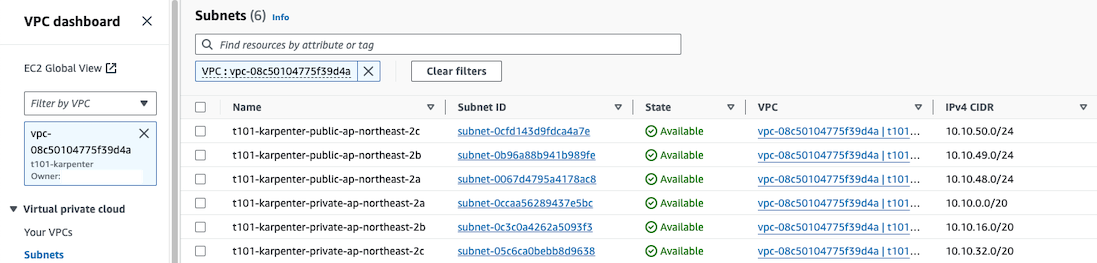 VPC 배포 결과
VPC 배포 결과
EKS 및 Fargate 배포
# EKS 배포
$ terraform apply -target="module.eks" -auto-approve
# => Apply complete! Resources: 24 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
# Outputs:
# configure_kubectl = "aws eks --region ap-northeast-2 update-kubeconfig --name t101-karpenter"
# 배포 확인
$ terraform state list
# => data.aws_availability_zones.available
# module.eks.data.aws_caller_identity.current
# module.eks.data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_role_policy[0]
# module.eks.data.aws_iam_session_context.current
# module.eks.data.aws_partition.current
# module.eks.data.tls_certificate.this[0]
# module.eks.aws_cloudwatch_log_group.this[0]
# module.eks.aws_ec2_tag.cluster_primary_security_group["Blueprint"]
# module.eks.aws_ec2_tag.cluster_primary_security_group["GithubRepo"]
# module.eks.aws_ec2_tag.cluster_primary_security_group["karpenter.sh/discovery"]
# module.eks.aws_eks_access_entry.this["cluster_creator"]
# module.eks.aws_eks_access_policy_association.this["cluster_creator_admin"]
# module.eks.aws_eks_cluster.this[0]
# module.eks.aws_iam_openid_connect_provider.oidc_provider[0]
# module.eks.aws_iam_policy.cluster_encryption[0]
# module.eks.aws_iam_role.this[0]
# module.eks.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.cluster_encryption[0]
# module.eks.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.this["AmazonEKSClusterPolicy"]
# module.eks.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.this["AmazonEKSVPCResourceController"]
# module.eks.time_sleep.this[0]
# module.vpc.aws_default_network_acl.this[0]
# module.vpc.aws_default_route_table.default[0]
# module.vpc.aws_default_security_group.this[0]
# module.vpc.aws_eip.nat[0]
# module.vpc.aws_internet_gateway.this[0]
# module.vpc.aws_nat_gateway.this[0]
# module.vpc.aws_route.private_nat_gateway[0]
# module.vpc.aws_route.public_internet_gateway[0]
# module.vpc.aws_route_table.private[0]
# module.vpc.aws_route_table.public[0]
# module.vpc.aws_route_table_association.private[0]
# module.vpc.aws_route_table_association.private[1]
# module.vpc.aws_route_table_association.private[2]
# module.vpc.aws_route_table_association.public[0]
# module.vpc.aws_route_table_association.public[1]
# module.vpc.aws_route_table_association.public[2]
# module.vpc.aws_subnet.private[0]
# module.vpc.aws_subnet.private[1]
# module.vpc.aws_subnet.private[2]
# module.vpc.aws_subnet.public[0]
# module.vpc.aws_subnet.public[1]
# module.vpc.aws_subnet.public[2]
# module.vpc.aws_vpc.this[0]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].data.aws_caller_identity.current
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_role_policy[0]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].data.aws_partition.current
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].data.aws_region.current
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].aws_eks_fargate_profile.this[0]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].aws_iam_role.this[0]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.this["AmazonEKSFargatePodExecutionRolePolicy"]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.this["AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy"]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].data.aws_caller_identity.current
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_role_policy[0]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].data.aws_partition.current
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].data.aws_region.current
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].aws_eks_fargate_profile.this[0]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].aws_iam_role.this[0]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.this["AmazonEKSFargatePodExecutionRolePolicy"]
# module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.this["AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy"]
# module.eks.module.kms.data.aws_caller_identity.current[0]
# module.eks.module.kms.data.aws_iam_policy_document.this[0]
# module.eks.module.kms.data.aws_partition.current[0]
# module.eks.module.kms.aws_kms_alias.this["cluster"]
# module.eks.module.kms.aws_kms_key.this[0]
$ terraform output
# => configure_kubectl = "aws eks --region ap-northeast-2 update-kubeconfig --name t101-karpenter"
# kubectl 설정
$ aws eks --region ap-northeast-2 update-kubeconfig --name t101-karpenter
$ cat ~/.kube/config
# k8s 노드, 파드 정보 확인
$ kubectl cluster-info
# => Kubernetes control plane is running at https://D858CEEA85279742B1B4738D555C8602.sk1.ap-northeast-2.eks.amazonaws.com
# CoreDNS is running at https://D858CEEA85279742B1B4738D555C8602.sk1.ap-northeast-2.eks.amazonaws.com/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
# To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
$ kubectl get node
# => No resources found
$ kubectl get pod -A
# => NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# kube-system coredns-5b9dfbf96-24qbm 0/1 Pending 0 22m
# kube-system coredns-5b9dfbf96-8q225 0/1 Pending 0 22m
$ kubectl describe pod coredns-5b9dfbf96-24 -n kube-system
# => ...
# Type Reason Age From Message
# ---- ------ ---- ---- -------
# Warning FailedScheduling 3m22s (x124 over 23m) default-scheduler no nodes available to schedule pods
# 상세 정보 확인
$ terraform show
$ terraform state list
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.data.aws_caller_identity.current'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.data.aws_iam_session_context.current'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_eks_cluster.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.data.tls_certificate.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_cloudwatch_log_group.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_eks_access_entry.this["cluster_creator"]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_iam_openid_connect_provider.oidc_provider[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.data.aws_partition.current'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_iam_policy.cluster_encryption[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_iam_role.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.time_sleep.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.kms.aws_kms_key.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.fargate_profile["kube_system"].aws_eks_fargate_profile.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.fargate_profile["karpenter"].aws_eks_fargate_profile.this[0]'
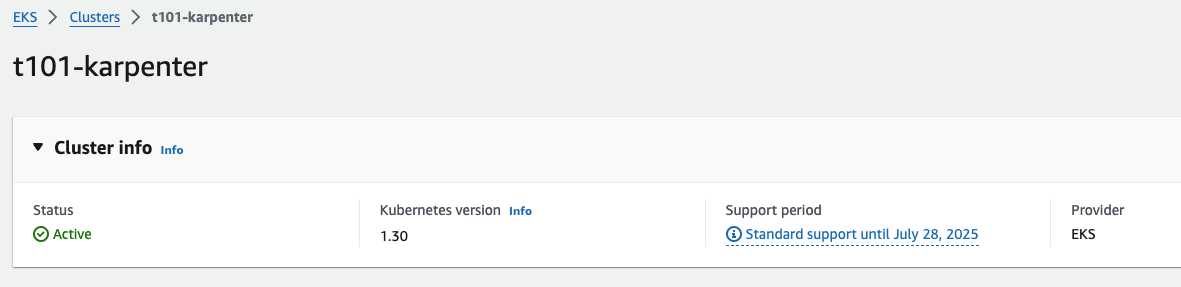 EKS 배포 결과
EKS 배포 결과
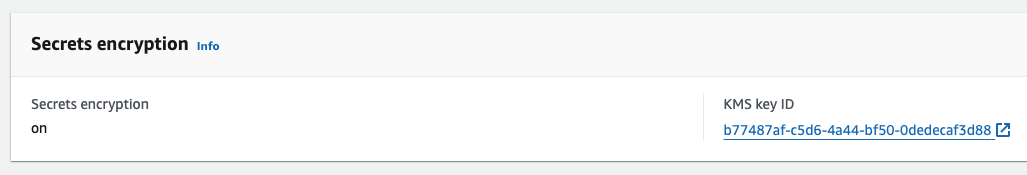 EKS 배포 결과 (Secret 암호화 관련) 설정
EKS 배포 결과 (Secret 암호화 관련) 설정
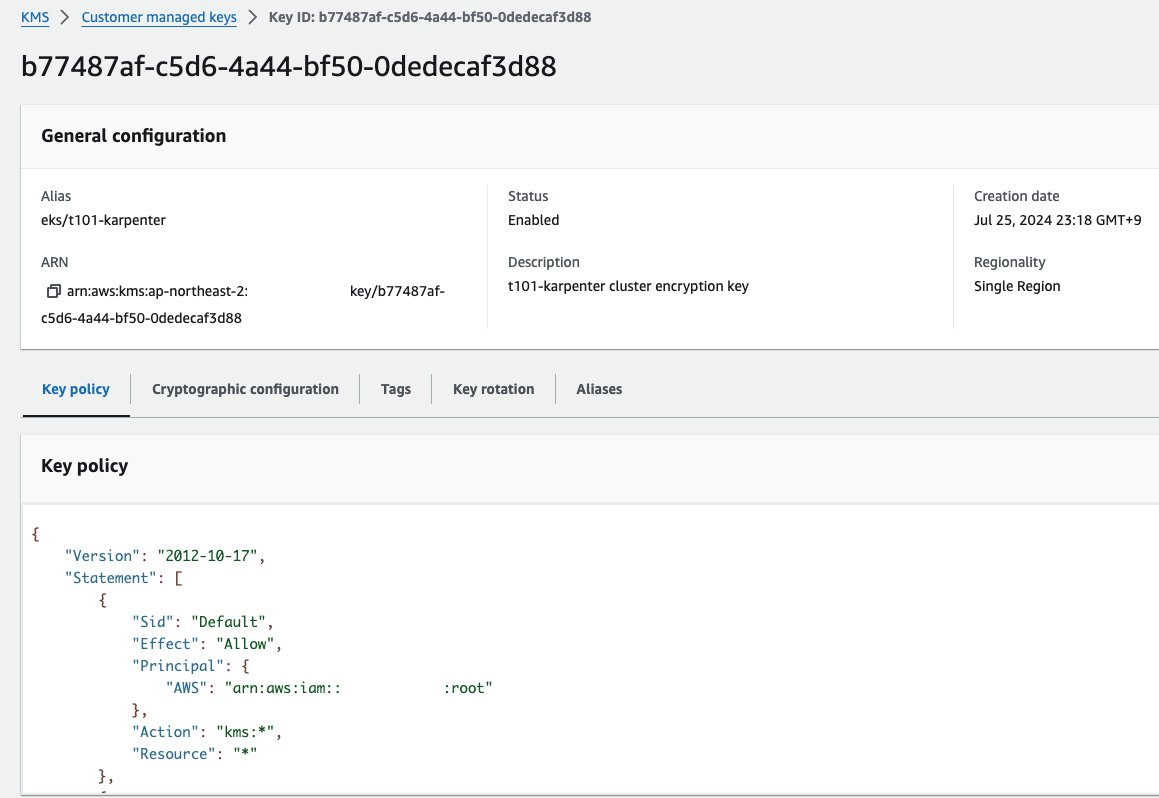 EKS 배포 결과 (Secret 암호화에 쓰이는 KMS 정보)
EKS 배포 결과 (Secret 암호화에 쓰이는 KMS 정보)
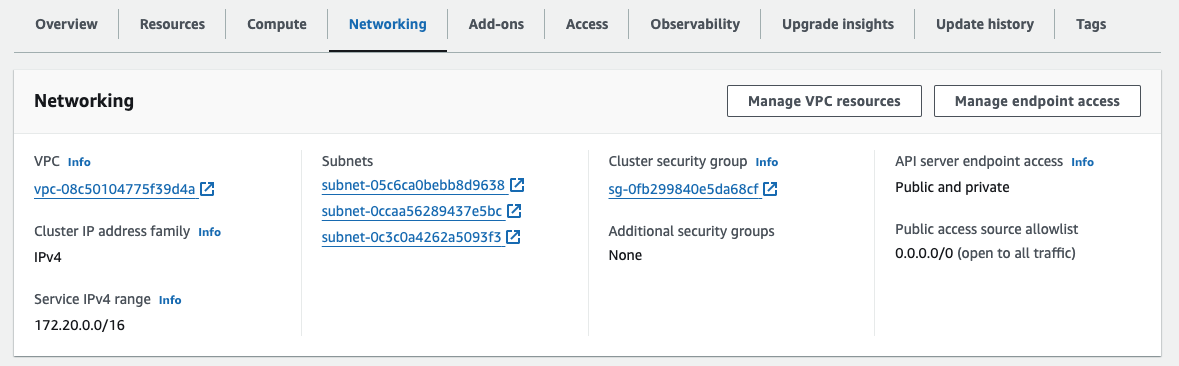 EKS 배포 결과 (네트워킹 정보)
EKS 배포 결과 (네트워킹 정보)
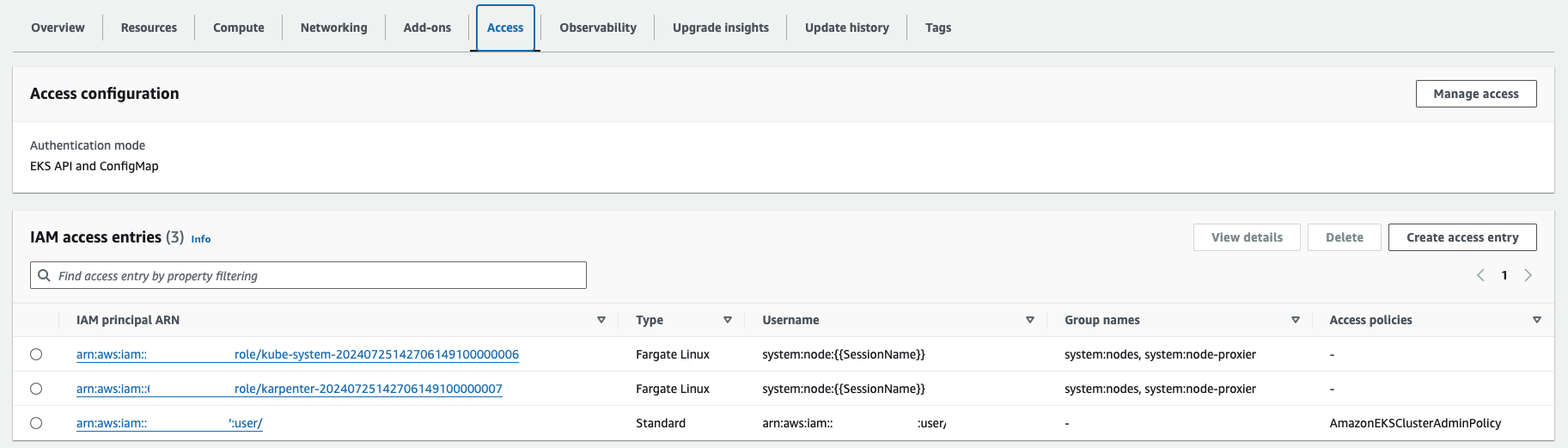 EKS 배포 결과 (접근 IAM 정보)
EKS 배포 결과 (접근 IAM 정보)
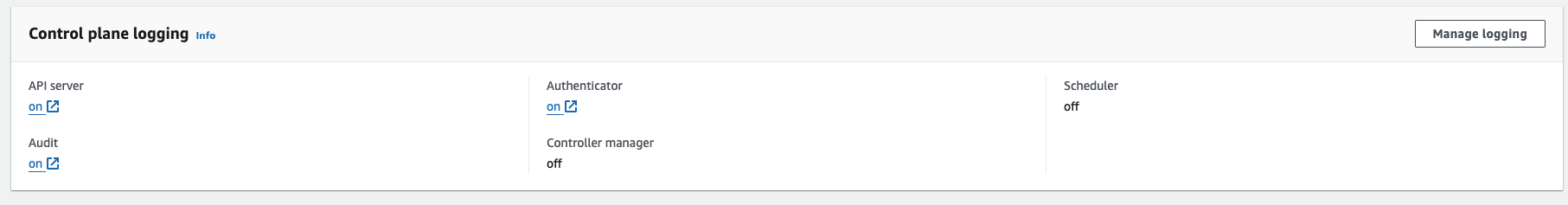 EKS 배포 결과 (로그 설정)
EKS 배포 결과 (로그 설정)
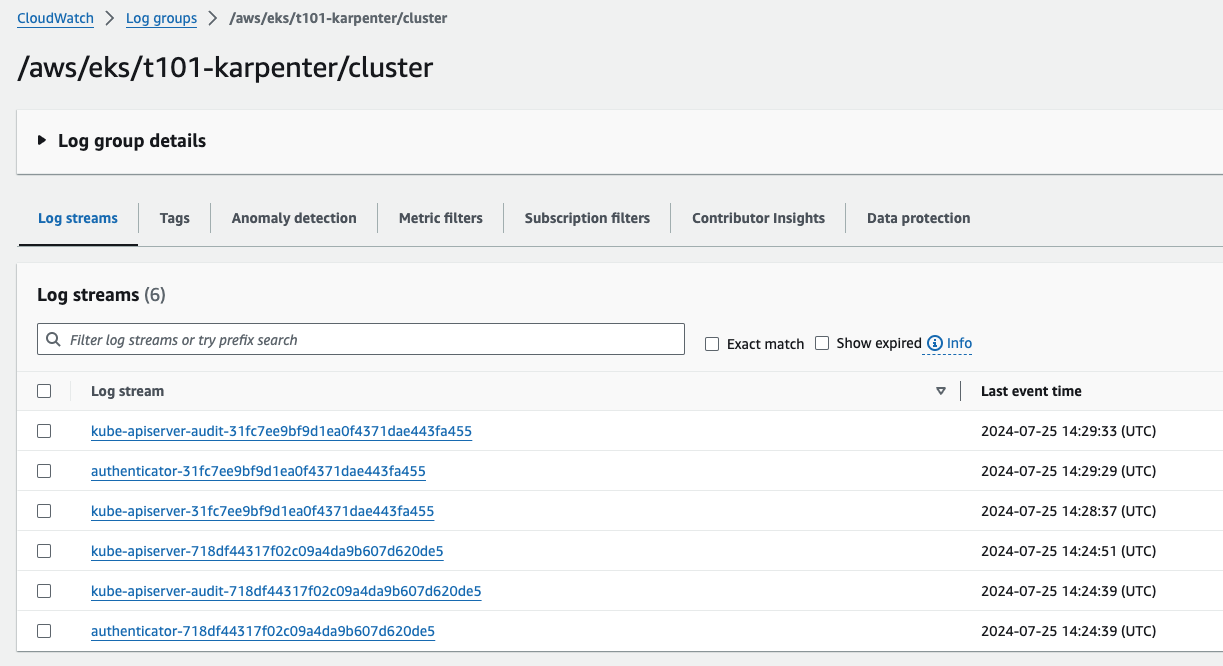 EKS 배포 결과 (Cloud Watch를 통한 로그 관리)
EKS 배포 결과 (Cloud Watch를 통한 로그 관리)
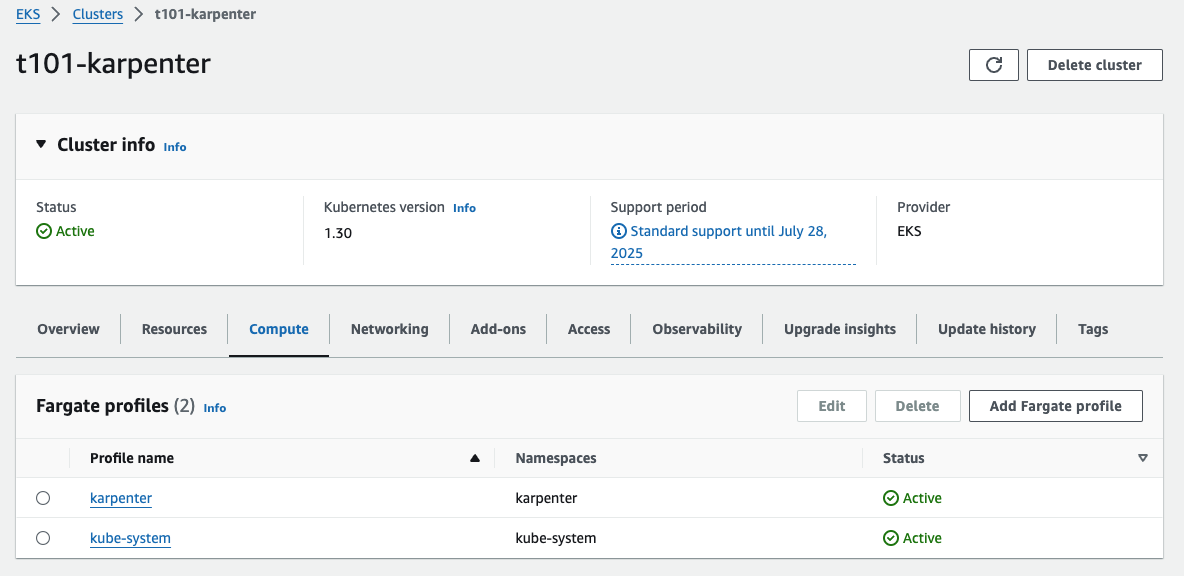 Fargate 배포 결과
Fargate 배포 결과
Karpenter 및 기타 addon 배포
# 배포
$ terraform apply -auto-approve
# 확인
$ terraform state list
# => data.aws_ecrpublic_authorization_token.token
# aws_eks_access_entry.karpenter_node_access_entry
# ...
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_caller_identity.current
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_eks_addon_version.this["coredns"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_eks_addon_version.this["kube-proxy"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_eks_addon_version.this["vpc-cni"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_iam_policy_document.karpenter[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_iam_policy_document.karpenter_assume_role[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_partition.current
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_region.current
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.karpenter["health_event"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.karpenter["instance_rebalance"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.karpenter["instance_state_change"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.karpenter["spot_interupt"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_target.karpenter["health_event"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_target.karpenter["instance_rebalance"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_target.karpenter["instance_state_change"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_target.karpenter["spot_interupt"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_eks_addon.this["coredns"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_eks_addon.this["kube-proxy"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_eks_addon.this["vpc-cni"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_iam_instance_profile.karpenter[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_iam_role.karpenter[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.karpenter["AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.karpenter["AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.karpenter["AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy"]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.time_sleep.this
# ...
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.data.aws_caller_identity.current[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.data.aws_iam_policy_document.this[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.data.aws_partition.current[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.aws_iam_policy.this[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.aws_iam_role.this[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.this[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.helm_release.this[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter_sqs.data.aws_iam_policy_document.this[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter_sqs.aws_sqs_queue.this[0]
# module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter_sqs.aws_sqs_queue_policy.this[0]
$ terraform show
# k8s 노드, 파드 정보 확인
$ kubectl cluster-info
# => Kubernetes control plane is running at https://D858CEEA85279742B1B4738D555C8602.sk1.ap-northeast-2.eks.amazonaws.com
# CoreDNS is running at https://D858CEEA85279742B1B4738D555C8602.sk1.ap-northeast-2.eks.amazonaws.com/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
#
# To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
$ kubectl get nodes -L node.kubernetes.io/instance-type -L topology.kubernetes.io/zone
# => NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INSTANCE-TYPE ZONE
# fargate-ip-10-10-18-179.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 4m58s v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2b
# fargate-ip-10-10-26-139.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 4m58s v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2b
# fargate-ip-10-10-41-162.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 4m51s v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2c
# fargate-ip-10-10-44-218.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 4m57s v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2c
# fargate를 프로비저닝하기 전에는 노드가 없었으나,
# fargate 프로비저닝 후 노드가 생성되었음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
$ kubectl get node -owide
# => NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
# fargate-ip-10-10-18-179.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 6m45s v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 10.10.18.179 <none> Amazon Linux 2 5.10.220-209.867.amzn2.x86_64 containerd://1.7.11
# fargate-ip-10-10-26-139.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 6m45s v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 10.10.26.139 <none> Amazon Linux 2 5.10.220-209.867.amzn2.x86_64 containerd://1.7.11
# fargate-ip-10-10-41-162.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 6m38s v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 10.10.41.162 <none> Amazon Linux 2 5.10.220-209.867.amzn2.x86_64 containerd://1.7.11
# fargate-ip-10-10-44-218.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 6m44s v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 10.10.44.218 <none> Amazon Linux 2 5.10.220-209.867.amzn2.x86_64 containerd://1.7.11
$ kubectl get pod -A -owide
# => NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
# karpenter karpenter-7c5786cbc4-q5k7x 1/1 Running 0 8m42s 10.10.18.179 fargate-ip-10-10-18-179.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
# karpenter karpenter-7c5786cbc4-vxlrq 1/1 Running 0 8m42s 10.10.26.139 fargate-ip-10-10-26-139.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
# kube-system coredns-86dcddd859-2x2gf 1/1 Running 0 8m43s 10.10.41.162 fargate-ip-10-10-41-162.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
# kube-system coredns-86dcddd859-xsdw5 1/1 Running 0 8m43s 10.10.44.218 fargate-ip-10-10-44-218.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
# node가 없어서 pod가 Pending 상태였던 것이,
# fargate로 프로비저닝되면서 fargate computing node가 생겨서 Running 상태로 변경되었음을 확인할 수 있습니다.
# helm chart 확인
$ helm list -n karpenter
# => NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
# karpenter karpenter 1 2024-07-25 23:54:59.19597 +0900 KST deployed karpenter-0.35.0 0.35.0
# 시크릿 확인 : kms로 암호 처리됨
$ kubectl get secret -n karpenter
# => NAME TYPE DATA AGE
# sh.helm.release.v1.karpenter.v1 helm.sh/release.v1 1 12m
$ kubectl get secret -n karpenter sh.helm.release.v1.karpenter.v1 -o json | jq
# 상세 정보 확인
$ terraform state list
$ terraform state show 'data.aws_ecrpublic_authorization_token.token'
$ terraform state show 'aws_eks_access_entry.karpenter_node_access_entry'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_caller_identity.current'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.data.aws_eks_addon_version.this["coredns"]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.karpenter["health_event"]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_cloudwatch_event_target.karpenter["health_event"]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_eks_addon.this["coredns"]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_iam_role.karpenter[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.aws_iam_instance_profile.karpenter[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.data.aws_iam_policy_document.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.aws_iam_policy.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter.helm_release.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter_sqs.aws_sqs_queue.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks_blueprints_addons.module.karpenter_sqs.aws_sqs_queue_policy.this[0]'
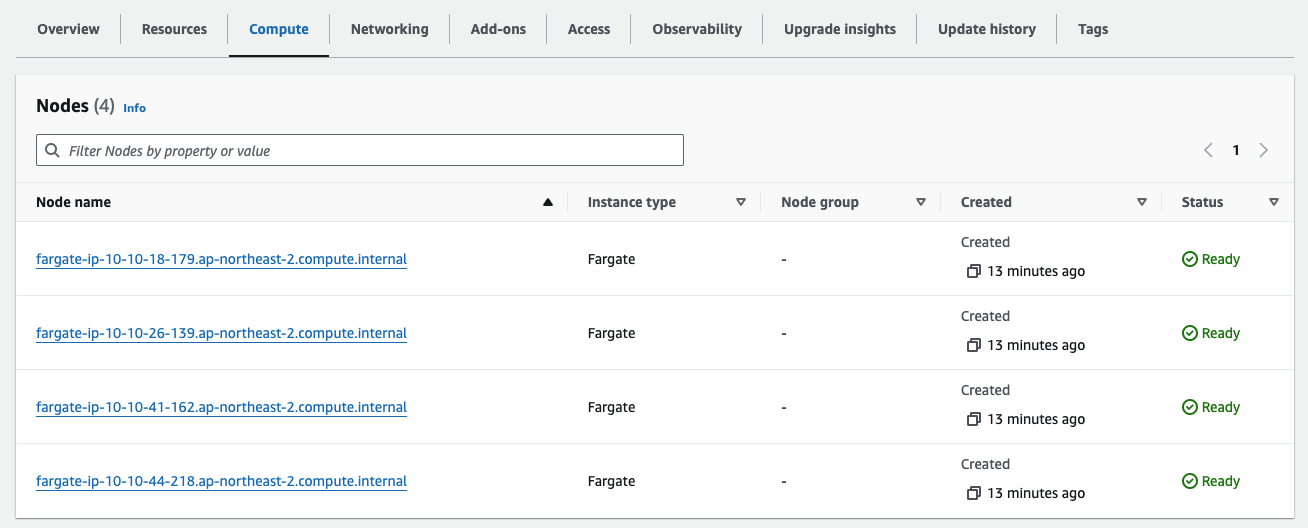 Karpenter 배포 결과
Karpenter 배포 결과
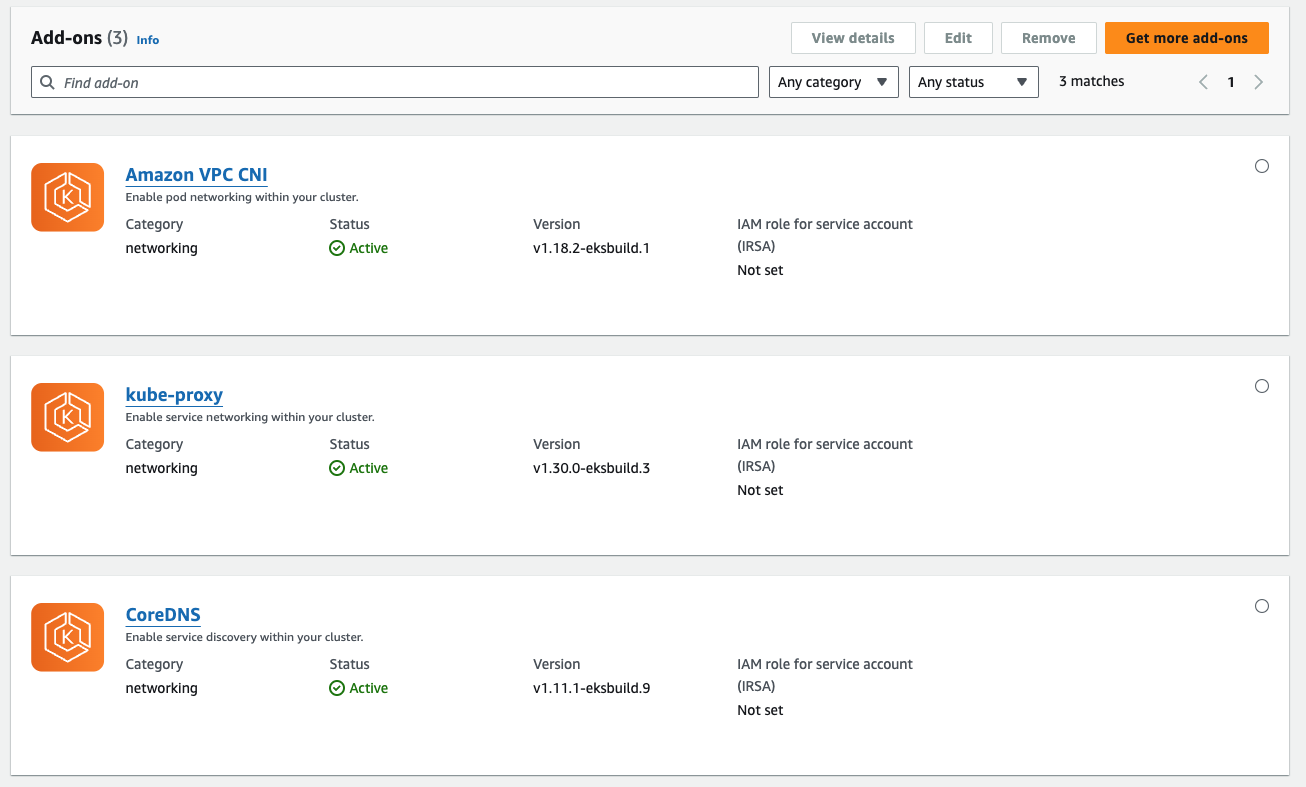 Addon 설치 결과
Addon 설치 결과
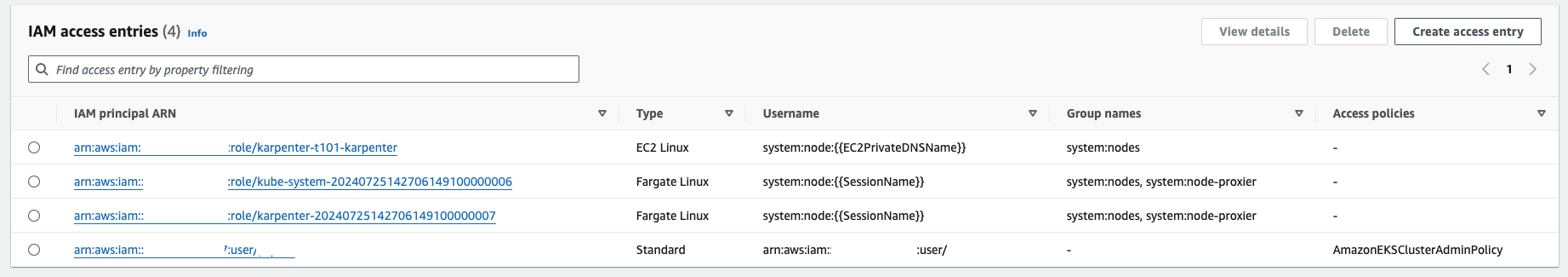 Karpenter 배포 결과 (접근 IAM 정보)
Karpenter 배포 결과 (접근 IAM 정보)
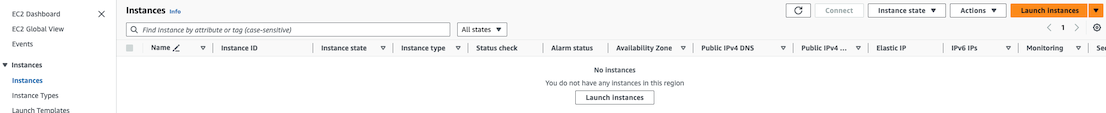 EC2 목록 (아직은 EC2 인스턴스가 없음)
EC2 목록 (아직은 EC2 인스턴스가 없음)
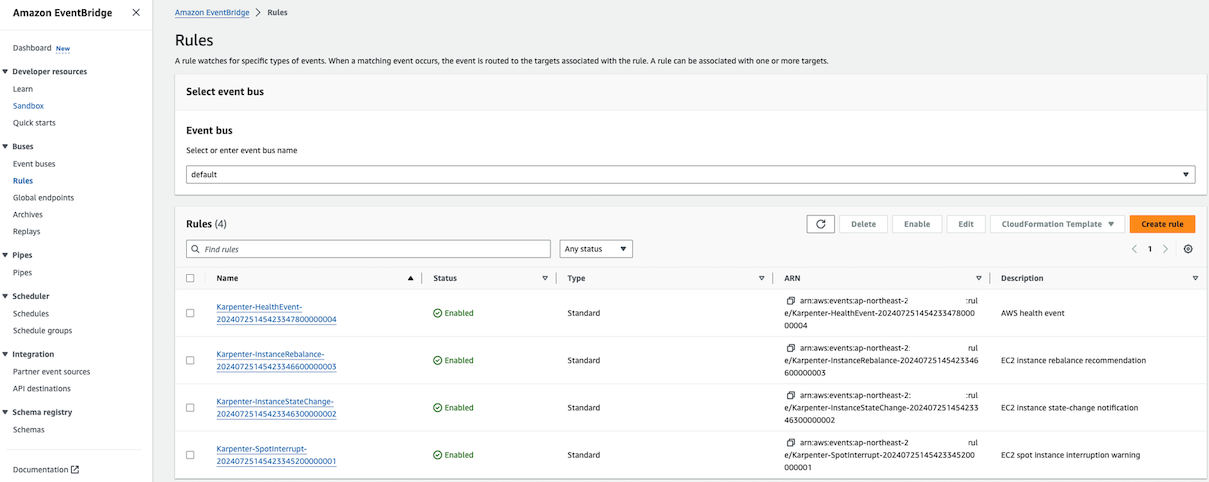 Karpenter의 Autoscaling 관련 룰
Karpenter의 Autoscaling 관련 룰
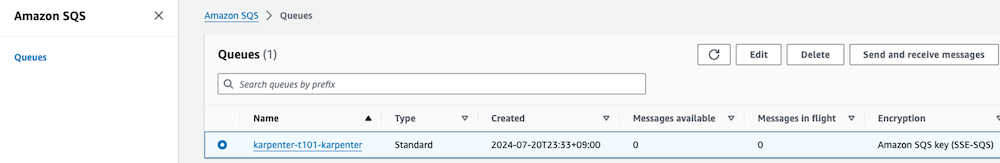 Karpenter의 SQS Queue
Karpenter의 SQS Queue
-
eks-node-viewer 설치 및 사용법
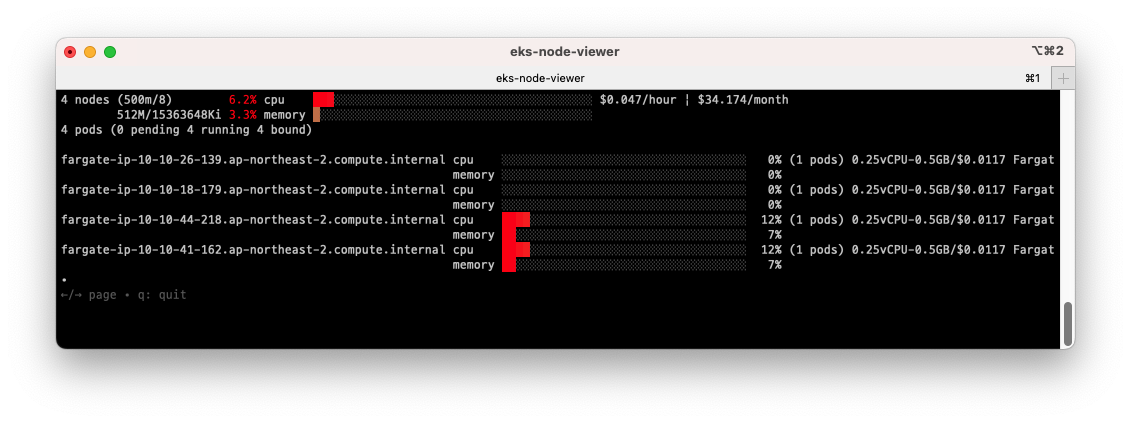 eks-node-viewer
eks-node-viewer- 노드 할당 가능 용량과 요청 request 리소스 표시해줍니다.
- 실제 파드의 리소스 사용량과는 차이가 있으니 참고용으로만 사용해야 할것입니다.
- 설치
# MacOS 기준 설치 $ brew tap aws/tap $ brew install eks-node-viewer - 사용
# [신규 터미널] Display both CPU and Memory Usage* eks-node-viewer --resources cpu,memory # Standard usage eks-node-viewer # Karpenter nodes only eks-node-viewer --node-selector karpenter.sh/nodepool # Display extra labels, i.e. AZ eks-node-viewer --extra-labels topology.kubernetes.io/zone # Sort by CPU usage in descending order eks-node-viewer --node-sort=eks-node-viewer/node-cpu-usage=dsc # Specify a particular AWS profile and region AWS_PROFILE=myprofile AWS_REGION=us-west-2
-
kube-ops-view 설치 및 사용법
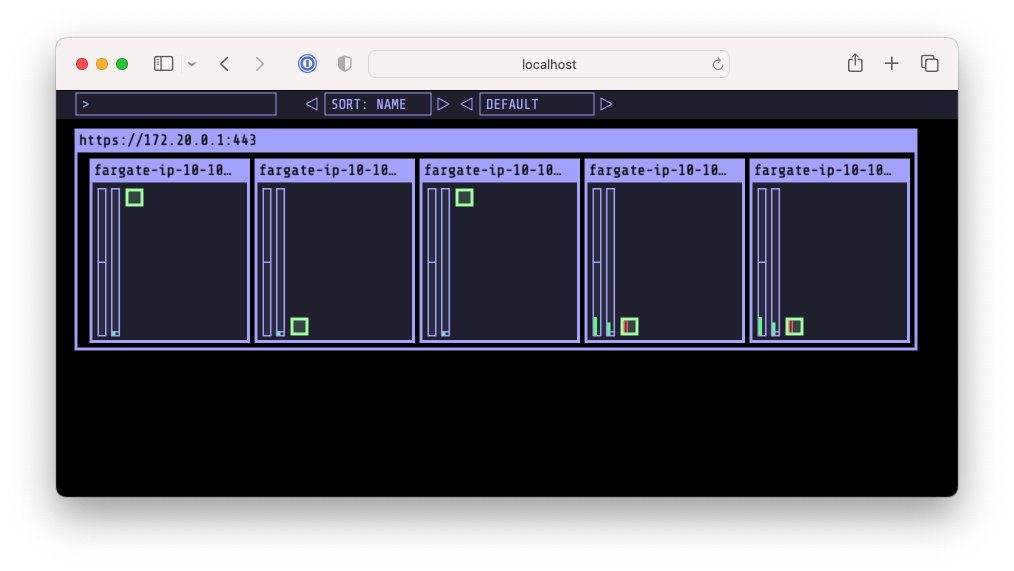 kube-ops-view
kube-ops-view- 노드의 파드 상태정보를 웹페이지에서 실시간으로 출력해줍니다.
- 설치 및 사용
$ helm repo add geek-cookbook https://geek-cookbook.github.io/charts/ # => "geek-cookbook" has been added to your repositories $ helm install kube-ops-view geek-cookbook/kube-ops-view --version 1.2.2 --set env.TZ="Asia/Seoul" --namespace kube-system # 포트포워딩 $ kubectl port-forward deployment/kube-ops-view -n kube-system 8080:8080 & # 접속 주소 확인 : 각각 1배, 1.5배, 3배 크기 $ echo -e "KUBE-OPS-VIEW URL = http://localhost:8080" $ echo -e "KUBE-OPS-VIEW URL = http://localhost:8080/#scale=1.5" $ echo -e "KUBE-OPS-VIEW URL = http://localhost:8080/#scale=3"
[실습] Karpenter on EKS Fargate
이번에는 Karpenter를 사용해 앞서 설치한 EKS와 Fargate로 구성한 클러스터를 관리해보겠습니다.
Karpenter는 AWS에서 제공하는 오픈소스 프로젝트로, Kubernetes 클러스터를 관리하는데 사용되는 오토스케일링 프로비저닝 엔진입니다. Node Auto Scaling과 비슷하나
AWS API를 통해 빠르고 효율적으로 워커노드를 스케일링하며, 높은 가용성, 비용최적화를 제공합니다. Karpenter 소개
먼저 replicas가 0인 pod를 생성하고, replica 수를 늘려서 Karpenter를 이용하여 autoscaling을 진행해보겠습니다.
- karpenter.yml 생성
# karpenter.yml --- apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1beta1 kind: EC2NodeClass metadata: name: default spec: amiFamily: AL2 role: karpenter-t101-karpenter subnetSelectorTerms: - tags: karpenter.sh/discovery: t101-karpenter securityGroupSelectorTerms: - tags: karpenter.sh/discovery: t101-karpenter tags: karpenter.sh/discovery: t101-karpenter --- apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1beta1 kind: NodePool metadata: name: default spec: template: spec: nodeClassRef: name: default requirements: - key: "karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-category" operator: In values: ["c", "m", "r"] - key: "karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-cpu" operator: In values: ["4", "8", "16", "32"] - key: "karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-hypervisor" operator: In values: ["nitro"] - key: "karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-generation" operator: Gt values: ["2"] limits: cpu: 1000 disruption: consolidationPolicy: WhenEmpty consolidateAfter: 30s - example.yml 생성
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: inflate spec: replicas: 0 selector: matchLabels: app: inflate template: metadata: labels: app: inflate spec: terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0 containers: - name: inflate image: public.ecr.aws/eks-distro/kubernetes/pause:3.7 resources: requests: cpu: 1 - karpenter 실행
$ kubectl apply -f karpenter.yml # => ec2nodeclass.karpenter.k8s.aws/default created # nodepool.karpenter.sh/default created # 확인 $ kubectl get ec2nodeclass,nodepool # => NAME AGE # ec2nodeclass.karpenter.k8s.aws/default 98s # # NAME NODECLASS # nodepool.karpenter.sh/default default $ kubectl apply -f example.yml $ kubectl get deploy # => NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE # inflate 0/0 0 0 11s $ karpenter 컨트롤러 로그 확인 $ kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller # karpenter를 이용한 autoscaling 확인 $ kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas=3 && kubectl get pod -w # => deployment.apps/inflate scaled # NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE # inflate-66fb68585c-8wnvs 0/1 Pending 0 0s # inflate-66fb68585c-p5j7d 0/1 Pending 0 0s # inflate-66fb68585c-sdqzz 0/1 Pending 0 0s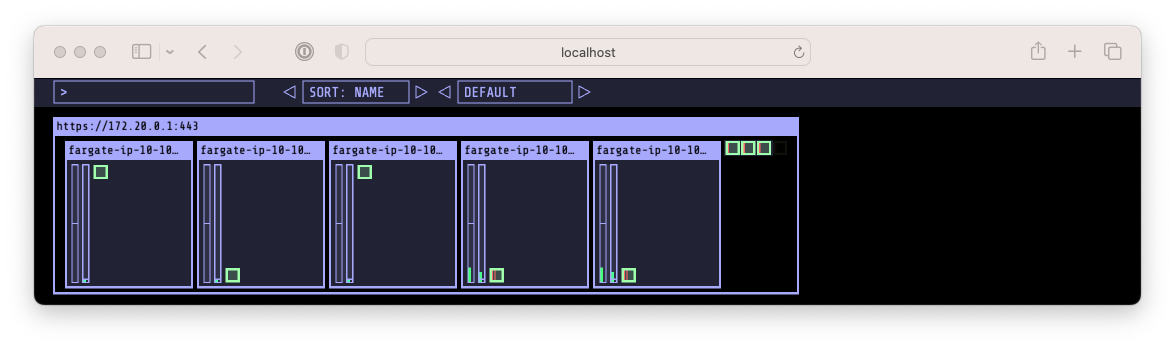 autoscaling 이 진행되지 않고 대기중인 모습
autoscaling 이 진행되지 않고 대기중인 모습- 위의 그림처럼 scaling 후 pending 상태로 오래 대기중이어서 log를 확인해보겠습니다.
# karpenter 컨트롤러 로그 확인 $ kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller # => { # "level":"ERROR","time":"2024-07-25T15:36:58.791Z", # ... # "error":"launching nodeclaim, creating instance, with fleet error(s), # AuthFailure.ServiceLinkedRoleCreationNotPermitted: # The provided credentials do not have permission to # create the service-linked role for EC2 Spot Instances." # }- 현재 ServiceLinkedRole 관련 기능이 없어서 생기는 문제 인것 같습니다. 아래의 명령을 실행하면 role이 생성되면서 오토 스케일링이 진행됩니다.
$ aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name spot.amazonaws.com
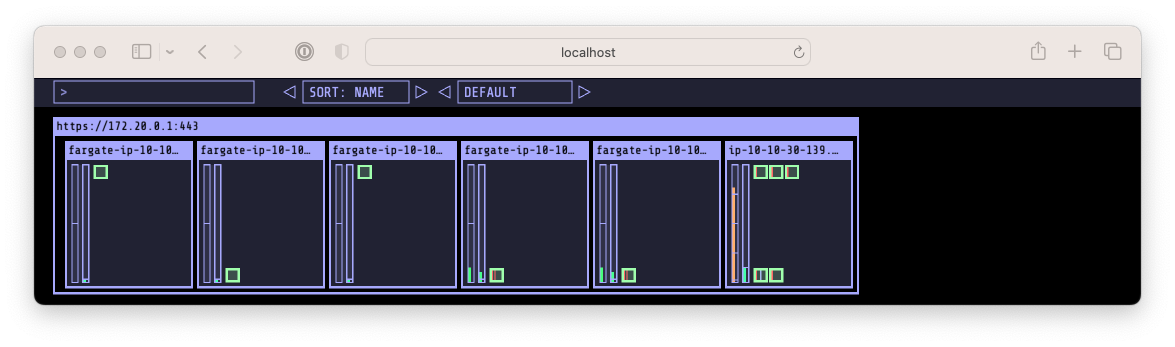 정상적으로 Autoscaling 된 결과
정상적으로 Autoscaling 된 결과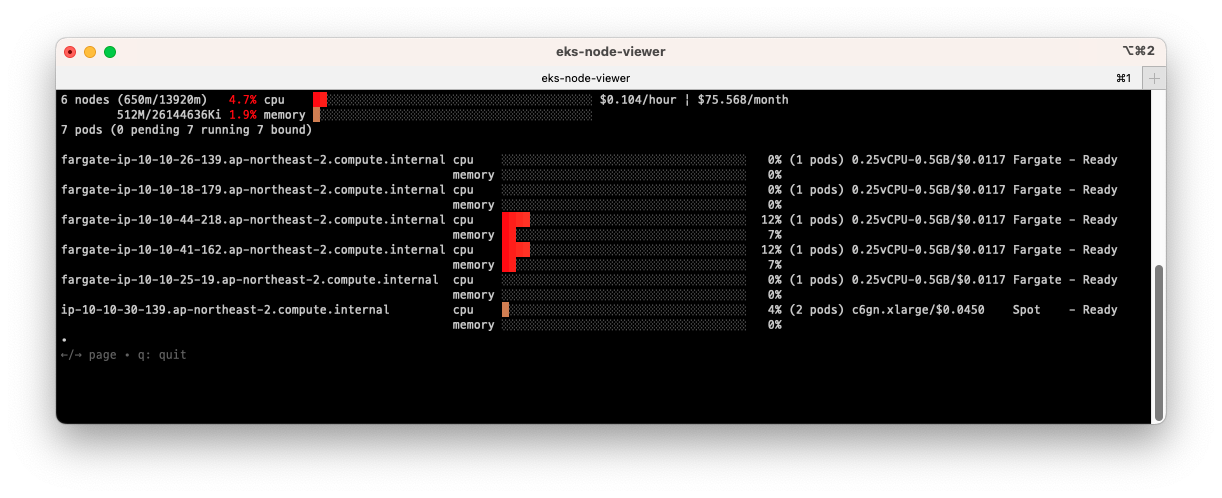 정상적으로 Autoscaling 된 결과 (Pod 상세 정보)
정상적으로 Autoscaling 된 결과 (Pod 상세 정보)- 위의 그림들 처럼 정상적으로 autoscaling이 진행되고, 5개 => 6개로 Node 가 추가되고 pod가 생성되어 실행되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
- 현재 ServiceLinkedRole 관련 기능이 없어서 생기는 문제 인것 같습니다. 아래의 명령을 실행하면 role이 생성되면서 오토 스케일링이 진행됩니다.
- 위의 그림처럼 scaling 후 pending 상태로 오래 대기중이어서 log를 확인해보겠습니다.
- karpenter 삭제
# $ kubectl get nodes -L karpenter.sh/nodepool -L node.kubernetes.io/instance-type -L topology.kubernetes.io/zone -L karpenter.sh/capacity-type # => NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION NODEPOOL INSTANCE-TYPE ZONE CAPACITY-TYPE # fargate-ip-10-10-18-179.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 53m v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2b # fargate-ip-10-10-25-19.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 30m v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2b # fargate-ip-10-10-26-139.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 53m v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2b # fargate-ip-10-10-41-162.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 53m v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2c # fargate-ip-10-10-44-218.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 53m v1.30.0-eks-404b9c6 ap-northeast-2c # ip-10-10-30-139.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 2m3s v1.30.0-eks-036c24b default c6gn.xlarge ap-northeast-2b spot # $ kubectl get nodeclaims # => default-mkbpj c6gn.xlarge ap-northeast-2b ip-10-10-30-139.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal True 18m $ kubectl get nodeclaims -o yaml | kubectl neat # deploy 삭제 >> 노드 변화 확인 해보기! $ kubectl delete -f example.yml # => deployment.apps "inflate" deleted # karpenter 정책 삭제 $ kubectl delete -f karpenter.yml # => ec2nodeclass.karpenter.k8s.aws "default" deleted # nodepool.karpenter.sh "default" deleted - 삭제
# kube-ops-view 삭제 $ helm uninstall kube-ops-view -n kube-system # addon & karpenter helm 삭제 $ terraform destroy -target="module.eks_blueprints_addons" -auto-approve # => Destroy complete! Resources: 24 destroyed. # EKS 삭제 $ terraform destroy -target="module.eks" -auto-approve # => Destroy complete! Resources: 24 destroyed. # VPC 삭제 : vpc 삭제가 잘 안될 경우 aws 콘솔에서 vpc 수동 삭제 -> vnic 등 남아 있을 경우 해당 vnic 강제 삭제 $ terraform destroy -auto-approve # => Destroy complete! Resources: 23 destroyed. # VPC 삭제 확인 $ aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filter 'Name=isDefault,Values=false' --output yaml # => Vpcs: [] # 잘 삭제되었습니다. # kubeconfig 삭제 $ rm -rf ~/.kube/config
EKS Workshop
- 이번에는 AWS에서 제공하는 EKS Workshop에서 소개하는 방법으로 EKS를 배포해보겠습니다.
- 관련링크 : EKS Workshop 소개, EKS Workshop Github, 유튜브
[실습] EKS 배포
사전준비
- awscli, terraform, kubectl 설치
- 코드 준비 Github
$ git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/eks-workshop-v2 $ cd eks-workshop-v2/cluster/terraform- providers.tf
provider "aws" { default_tags { tags = local.tags } } terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = ">= 4.67.0" } } required_version = ">= 1.4.2" } - variables.tf - cluster 이름, cluster 버전, ami 버전, vpc cidr 변경 가능
variable "cluster_name" { description = "Name of the EKS cluster" type = string default = "t101-eks-workshop" } variable "cluster_version" { description = "EKS cluster version." type = string default = "1.30" } variable "ami_release_version" { description = "Default EKS AMI release version for node groups" type = string default = "1.30.0-20240625" } variable "vpc_cidr" { description = "Defines the CIDR block used on Amazon VPC created for Amazon EKS." type = string default = "10.42.0.0/16" } - vpc.tf
locals { private_subnets = [for k, v in local.azs : cidrsubnet(var.vpc_cidr, 3, k + 3)] public_subnets = [for k, v in local.azs : cidrsubnet(var.vpc_cidr, 3, k)] azs = slice(data.aws_availability_zones.available.names, 0, 3) } data "aws_availability_zones" "available" { state = "available" } module "vpc" { source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws" version = "~> 5.1" name = var.cluster_name cidr = var.vpc_cidr azs = local.azs public_subnets = local.public_subnets private_subnets = local.private_subnets public_subnet_suffix = "SubnetPublic" private_subnet_suffix = "SubnetPrivate" enable_nat_gateway = true create_igw = true enable_dns_hostnames = true single_nat_gateway = true # Manage so we can name manage_default_network_acl = true default_network_acl_tags = { Name = "${var.cluster_name}-default" } manage_default_route_table = true default_route_table_tags = { Name = "${var.cluster_name}-default" } manage_default_security_group = true default_security_group_tags = { Name = "${var.cluster_name}-default" } public_subnet_tags = merge(local.tags, { "kubernetes.io/role/elb" = "1" }) private_subnet_tags = merge(local.tags, { "karpenter.sh/discovery" = var.cluster_name }) tags = local.tags } - main.tf
locals { tags = { created-by = "eks-workshop-v2" study = "t101" # 태그 추가 for = "Sweet Little Bird" env = var.cluster_name } } - eks.tf
module "eks" { source = "terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws" version = "~> 20.0" cluster_name = var.cluster_name cluster_version = var.cluster_version cluster_endpoint_public_access = true cluster_addons = { vpc-cni = { before_compute = true most_recent = true configuration_values = jsonencode({ env = { ENABLE_POD_ENI = "true" ENABLE_PREFIX_DELEGATION = "true" POD_SECURITY_GROUP_ENFORCING_MODE = "standard" } nodeAgent = { enablePolicyEventLogs = "true" } enableNetworkPolicy = "true" }) } } vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id subnet_ids = module.vpc.private_subnets create_cluster_security_group = false create_node_security_group = false eks_managed_node_groups = { default = { instance_types = ["m5.large"] force_update_version = true release_version = var.ami_release_version min_size = 3 max_size = 6 desired_size = 3 update_config = { max_unavailable_percentage = 50 } labels = { workshop-default = "yes" } } } tags = merge(local.tags, { "karpenter.sh/discovery" = var.cluster_name }) }
- providers.tf
terraform init
테라폼을 사용하기위해 초기화하고, 설치된 모듈 및 프로바이더 정보를 확인해보겠습니다.
$ terraform init
$ tree .terraform
# 설치된 모듈 확인
$ cat .terraform/modules/modules.json | jq
# 설치된 프로바이더 및 버전 확인
$ tree .terraform/providers/registry.terraform.io/hashicorp -L 2
# => .terraform/providers/registry.terraform.io/hashicorp
# ├── aws
# │ └── 5.60.0
# ├── cloudinit
# │ └── 2.3.4
# ├── null
# │ └── 3.2.2
# ├── time
# │ └── 0.12.0
# └── tls
# └── 4.0.5
VPC 배포
VPC를 먼저 배포하고 관련 정보를 확인해보겠습니다. EKS와 한꺼번에 배포해도 되지만 진행 상황을 확인하기 위해 VPC를 먼저 배포해보겠습니다.
# 설치전 VPC 정보 확인
$ aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filter 'Name=isDefault,Values=false' --output yaml
# => Vpcs: [] # 현재 VPC가 없습니다.
# VPC 배포
$ terraform apply -target="module.vpc" -auto-approve
# => Apply complete! Resources: 23 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
# 배포 확인
$ terraform state list
$ terraform show
$ aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filter 'Name=isDefault,Values=false' --output yaml
# => Vpcs:
# - CidrBlock: 10.42.0.0/16
# CidrBlockAssociationSet:
# - AssociationId: vpc-cidr-assoc-0c375c03935938c89
# CidrBlock: 10.42.0.0/16
# ...
# State: available
# Tags:
# ...
# - Key: study # 추가한 태그 확인
# Value: t101
# - Key: Name
# Value: t101-eks-workshop
# VpcId: vpc-0247fb591c49eab40
# 사용가능한 가용성 존 확인
$ echo "data.aws_availability_zones.available" | terraform console
# VPC/subnet 상세 정보 및 tag 확인
$ terraform state show 'module.vpc.aws_vpc.this[0]'
$ VPCID=$(echo module.vpc.vpc_id | terraform console) # 현재 VPC ID를 $VPCID 변수에 저장
# VPC 의 Subnet 상세 정보 확인 (json)
$ aws ec2 describe-subnets --filters "Name=vpc-id,Values=$VPCID" | jq
# VPC 의 Subnet 상세 정보 확인 (텍스트)
$ aws ec2 describe-subnets --filters "Name=vpc-id,Values=$VPCID" --output text
# public 서브넷과 private 서브넷 CIDR 확인
$ terraform state show 'module.vpc.aws_subnet.public[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.vpc.aws_subnet.private[0]'
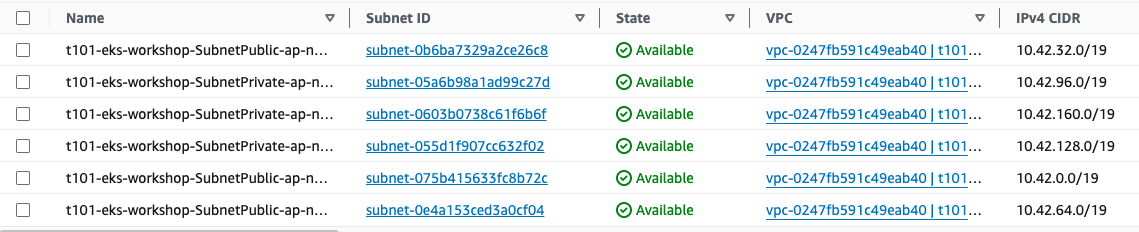 VPC 배포 결과 (subnet)
VPC 배포 결과 (subnet)
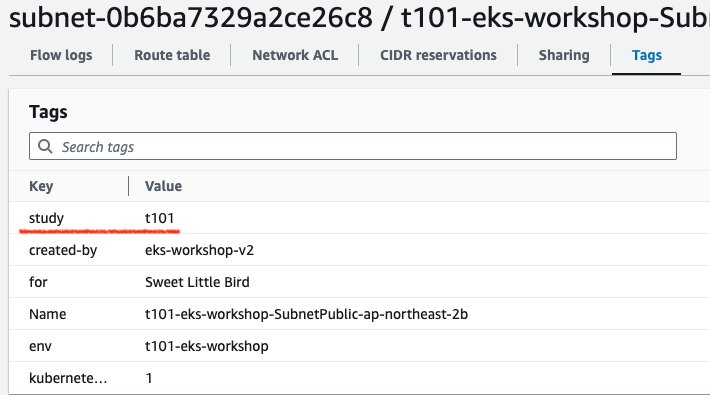 VPC 배포 결과 (subnet 태그 정보)
VPC 배포 결과 (subnet 태그 정보)
EKS 배포
# EKS 배포
$ terraform apply -auto-approve
# => Apply complete! Resources: 24 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
# EKS 배포 확인
$ terraform state list
# => data.aws_availability_zones.available
# module.eks.data.aws_caller_identity.current
# module.eks.data.aws_eks_addon_version.this["vpc-cni"]
# module.eks.data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_role_policy[0]
# module.eks.data.aws_iam_session_context.current
# module.eks.data.aws_partition.current
# module.eks.data.tls_certificate.this[0]
# module.eks.aws_cloudwatch_log_group.this[0]
# module.eks.aws_ec2_tag.cluster_primary_security_group["created-by"]
# module.eks.aws_ec2_tag.cluster_primary_security_group["env"]
# module.eks.aws_ec2_tag.cluster_primary_security_group["karpenter.sh/discovery"]
# module.eks.aws_ec2_tag.cluster_primary_security_group["study"]
# module.eks.aws_eks_addon.before_compute["vpc-cni"]
# module.eks.aws_eks_cluster.this[0]
# module.eks.aws_iam_openid_connect_provider.oidc_provider[0]
# module.eks.aws_iam_policy.cluster_encryption[0]
# module.eks.aws_iam_role.this[0]
# ...
# module.eks.module.kms.data.aws_caller_identity.current[0]
# module.eks.module.kms.data.aws_iam_policy_document.this[0]
# module.eks.module.kms.data.aws_partition.current[0]
# module.eks.module.kms.aws_kms_alias.this["cluster"]
# module.eks.module.kms.aws_kms_key.this[0]
# module.eks.module.eks_managed_node_group["default"].module.user_data.null_resource.validate_cluster_service_cidr
# EKS 자격 증명 설정 및 확인
## aws eks --region <REGION> update-kubeconfig --name <CLUSTER_NAME> --alias <CLUSTER_NAME>
$ aws eks --region ap-northeast-2 update-kubeconfig --name t101-eks-workshop
$ cat ~/.kube/config
# k8s 클러스터 정보 확인
$ kubectl cluster-info
# => error: You must be logged in to the server (Unauthorized)
정상적으로 배포하였고 EKS 자격증명을 설정하였음에도 kubectl 사용시 권한이 없다고 나옵니다.
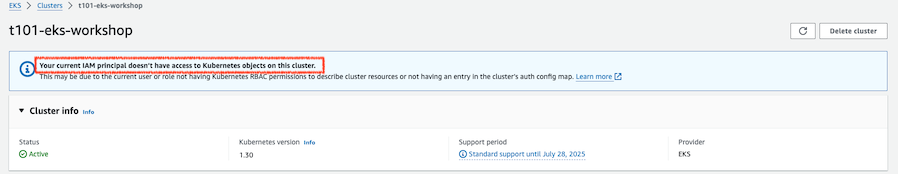
또한 EKS 콘솔에서도 권한이 없다고 나옵니다. 이는 현재 사용중인 IAM이 해당 k8s 클러스터에 대한 권한이 없기 때문입니다. 권한을 부여하는 작업을 진행하고 계속 배포상태를 확인해보겠습니다.
# EKS 관리용 IAM User 의 access entry 생성
$ ACCOUNT_ID=$(aws sts get-caller-identity --query 'Account' --output text)
# $ MYIAMUSER=<각자 자신의 IAM User>
$ MYIAMUSER=admin
$ echo $ACCOUNT_ID $MYIAMUSER
$ aws eks create-access-entry --cluster-name t101-eks-workshop --principal-arn arn:aws:iam::${ACCOUNT_ID}:user/${MYIAMUSER}
$ aws eks list-access-entries --cluster-name t101-eks-workshop
# EKS 관리용 IAM User에 AmazonEKSClusterAdminPolicy 연동
$ aws eks associate-access-policy --cluster-name t101-eks-workshop --principal-arn arn:aws:iam::${ACCOUNT_ID}:user/${MYIAMUSER} \
--policy-arn arn:aws:eks::aws:cluster-access-policy/AmazonEKSClusterAdminPolicy --access-scope type=cluster
$ aws eks list-associated-access-policies --cluster-name t101-eks-workshop --principal-arn arn:aws:iam::${ACCOUNT_ID}:user/${MYIAMUSER} | jq
$ aws eks describe-access-entry --cluster-name t101-eks-workshop --principal-arn arn:aws:iam::${ACCOUNT_ID}:user/${MYIAMUSER} | jq
# (참고) context name 변경
$ kubectl config rename-context "arn:aws:eks:ap-northeast-2:$(aws sts get-caller-identity --query 'Account' --output text):cluster/t101-eks-workshop" "T101-Lab"
# => Context "arn:aws:eks:ap-northeast-2:123456:cluster/t101-eks-workshop" renamed to "T101-Lab".
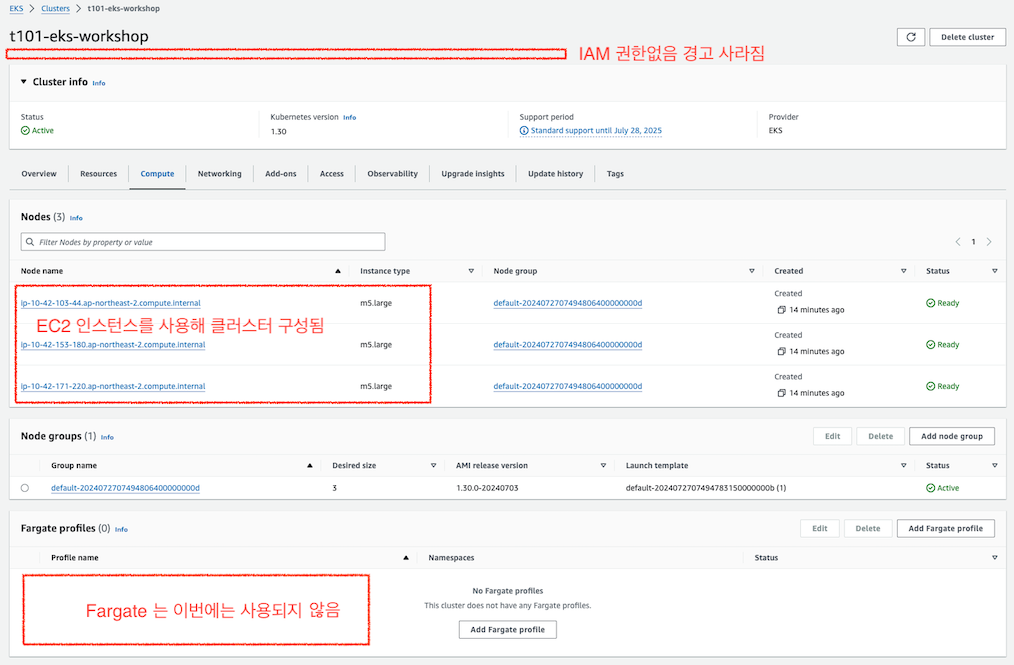
# k8s 클러스터, 노드, 파드 정보 확인 - 이제 정상적으로 조회 됩니다.
$ kubectl cluster-info
# => Kubernetes control plane is running at https://79B209921C6987FCA6A542FDE1272C2E.gr7.ap-northeast-2.eks.amazonaws.com
# CoreDNS is running at https://79B209921C6987FCA6A542FDE1272C2E.gr7.ap-northeast-2.eks.amazonaws.com/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
$ kubectl get node
$ kubectl get nodes -L node.kubernetes.io/instance-type -L topology.kubernetes.io/zone
# => NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INSTANCE-TYPE ZONE
# ip-10-42-103-44.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 16m v1.30.0-eks-036c24b m5.large ap-northeast-2a
# ip-10-42-153-180.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 16m v1.30.0-eks-036c24b m5.large ap-northeast-2b
# ip-10-42-171-220.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal Ready <none> 16m v1.30.0-eks-036c24b m5.large ap-northeast-2c
$ kubectl get pod -A
# => NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# kube-system aws-node-2jnd5 2/2 Running 0 16m
# kube-system aws-node-ftb8g 2/2 Running 0 16m
# kube-system aws-node-gn6nx 2/2 Running 0 16m
# kube-system coredns-5b9dfbf96-f8bfr 1/1 Running 0 19m
# kube-system coredns-5b9dfbf96-rtwfs 1/1 Running 0 19m
# kube-system kube-proxy-5zkxj 1/1 Running 0 16m
# kube-system kube-proxy-n645w 1/1 Running 0 16m
# kube-system kube-proxy-rcbvk 1/1 Running 0 16m
# 상세 정보 확인
$ terraform show
$ terraform state list
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_ec2_tag.cluster_primary_security_group["study"]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_eks_addon.before_compute["vpc-cni"]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_eks_cluster.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_iam_openid_connect_provider.oidc_provider[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.aws_iam_policy.cluster_encryption[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.time_sleep.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.eks_managed_node_group["default"].aws_eks_node_group.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.eks_managed_node_group["default"].aws_iam_role.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.eks_managed_node_group["default"].aws_launch_template.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.eks_managed_node_group["default"].module.user_data.null_resource.validate_cluster_service_cidr'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.kms.aws_kms_key.this[0]'
$ terraform state show 'module.eks.module.kms.aws_kms_alias.this["cluster"]'
kube-ops-view 설치 및 사용
앞서 설치해보았던 kube-ops-view를 이번 kubernetes 클러스터에도 설치해보겠습니다.
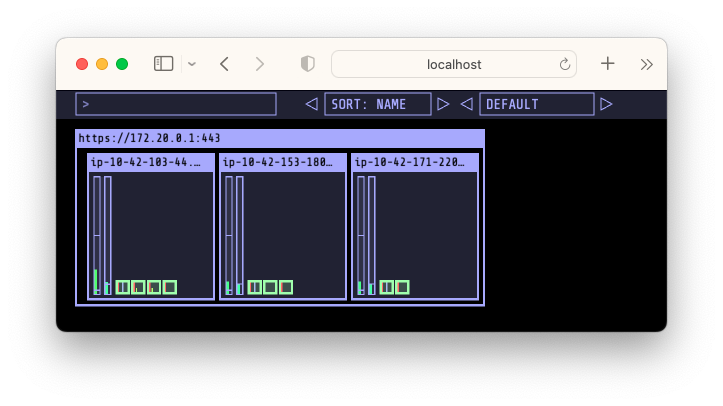 kube-ops-view
kube-ops-view
- 노드의 파드 상태정보를 웹페이지에서 실시간으로 출력해줍니다.
- 설치 및 사용
$ helm repo add geek-cookbook https://geek-cookbook.github.io/charts/ # => "geek-cookbook" has been added to your repositories $ helm install kube-ops-view geek-cookbook/kube-ops-view --version 1.2.2 --set env.TZ="Asia/Seoul" --namespace kube-system # 포트포워딩 $ kubectl port-forward deployment/kube-ops-view -n kube-system 8080:8080 & # 접속 주소 확인 : 각각 1배, 1.5배, 3배 크기 $ echo -e "KUBE-OPS-VIEW URL = http://localhost:8080" $ echo -e "KUBE-OPS-VIEW URL = http://localhost:8080/#scale=1.5" $ echo -e "KUBE-OPS-VIEW URL = http://localhost:8080/#scale=3"
Pod 배포
EKS Blueprint에서 제공하는 예제를 이용하여 Pod를 배포해보겠습니다.
- example.yml 생성
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: inflate spec: replicas: 0 selector: matchLabels: app: inflate template: metadata: labels: app: inflate spec: terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0 containers: - name: inflate image: public.ecr.aws/eks-distro/kubernetes/pause:3.7 resources: requests: cpu: 1 - Pod 배포 실습
$ kubectl create -f example.yml # => deployment.apps/inflate created $ kubectl get deploy # replicas가 0이어서 생성된 pod가 없습니다. # => NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE # inflate 0/0 0 0 16s # 3개로 scale 해보겠습니다. $ kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas=3 && kubectl get pod -w # => deployment.apps/inflate scaled # NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE # inflate-66fb68585c-8j7wr 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s # inflate-66fb68585c-j6bh4 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s # inflate-66fb68585c-sqwmc 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1s # ... 잠시후 ... # inflate-66fb68585c-8j7wr 1/1 Running 0 4s # inflate-66fb68585c-j6bh4 1/1 Running 0 5s # inflate-66fb68585c-sqwmc 1/1 Running 0 5s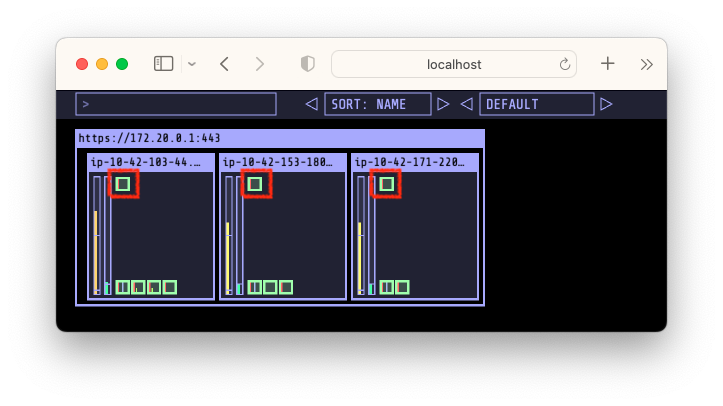 Pod 배포 결과
Pod 배포 결과
EKS 클러스터 및 VPC 삭제
# kube-ops-view 삭제
$ helm uninstall kube-ops-view -n kube-system
# => release "kube-ops-view" uninstalled
# 삭제 : vpc 삭제가 잘 안될 경우 aws 콘솔에서 vpc 수동 삭제 -> vnic 등 남아 있을 경우 해당 vnic 강제 삭제 : 9분 소요
$ terraform destroy -auto-approve
# => Destroy complete! Resources: 47 destroyed.
# VPC 삭제 확인
$ aws ec2 describe-vpcs --filter 'Name=isDefault,Values=false' --output yaml
# => Vpcs: []
# kubeconfig 삭제
$ rm -rf ~/.kube/config
마치며
이번 주에는 EKS Blueprint를 이용한 방법과 EKS Workshop을 이용한 방법을 통해 Terraform을 활용하여 EKS 배포를 진행해보았습니다. 이번 실습을 통해 놀란점은 EKS 배포가 참 복잡하고 많은 AWS 기능을 사용해야 하는구나 하는것과 Terraform을 활용하면 이렇게 쉽게 클러스터를 배포 할 수 있구나 하는것입니다.
아무리 복잡한 배포 과정이 필요하더라도 Terraform 모듈을 잘 만들어두면 이후에는 누구라도 쉽게 몇 줄의 명령어 만으로 배포가 가능하다는 것을 느꼈고 Terraform의 강력함을 느꼈습니다.
이번 실습을 거치면서 AWS와 Terraform에 대해 조금더 알게 되었고, 한 발자국 더 가까워진 느낌입니다. 좋은 실습 기회를 주신 가시다 님과 Terraform 101 스터디를 진행하신 분들께 감사드립니다. 다음 스터디가 마지막이어서 아쉽기도 하면서 기대도 됩니다. 마지막까지 열심히 달려보겠습니다.
